Carrier concentration formula in hall effect
October 28 2020 by Electrical4U. Figure 812 Hall effect At equilibrium the Lorentz force on a carrier FL Bevd _________ 8113 and the Hall force FH eEH _________ 8114 where EH is the Hall.

What Is Hall Effect Hall Angle Applications Of Hall Effect Electronics Coach
A current is made to flow through the sample material and the voltage.

. At temperature TK in an intrinsic semiconductor n p ni where ni is called. Department of Energys Office of Scientific and Technical Information. In our experiment we use the van der Pauw method.
The need to determine accurately support the importance of the Hall effect. The results of Hall effect measurements of PbSnTePbTe are shown in Fig. σ n 1ρ n neμ dont confuse ρ with p.
Going back to the Hall effect if the current in the strip is I then from Current and Resistance we know that 1173 I n e v d A where n is the number of charge carriers per. The electron and hole concentration remain constant as long as the temperature remain constant. Carrier concentrations nand p How do we measure n p μ n and μ p Through conductivity resistivity measurements.
Note also that the Hall field is large for low carrier concentrations. Naivly assume one type of carrier and plug into the formula R H 1ne this yields a carrier concentra-tion of 4296 8109 1588 10 cm 3 wchich is about 1000 times greater than the. The carrier concentration at 77 K reaches a minimum at 3110 3 PTe 1410 3 torr for Tg 600.
And the mobility of carriers in semiconductors. The DC Hall effect is an important phenomenon in condensed matter physics which allows us to measure properties of a semiconductor. Hence the Hall voltage at B 1T and i10A and t 1 mm for copper and Silicone are 06µV and 6 mV respectively.
The Hall voltage is much more measurable in. Problem that this formula generalizes to a wide class of materials. We might expect that the effect will be harder to detect in.
The Hall Effect studies on Zn-Te thin films of different composition and thicknesses have been made at room temperature for different magnetic fields between 3 to 95 K Gauss at different. This develop a potential difference along y-axis is known as Hall voltage VH and this effect is called Hall Effect. Whenever we place a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field there is a deflection of the charge carriers due influence of.

Hall Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Hall Effect Applications Of Hall Effect Electrical4u
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor

The Van Der Pauw Method Of Measuring Hall Effect To Determine Mobility Carrier Type Concentration Youtube

Hall Effect Coefficient An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Hall Effect Measurements In Materials Characterization Eetimes

Electromagnetism Can Someone Help Me Understand This Simple Derivation For Hall Voltage Physics Stack Exchange
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor

What Is Hall Effect Hall Angle Applications Of Hall Effect Electronics Coach
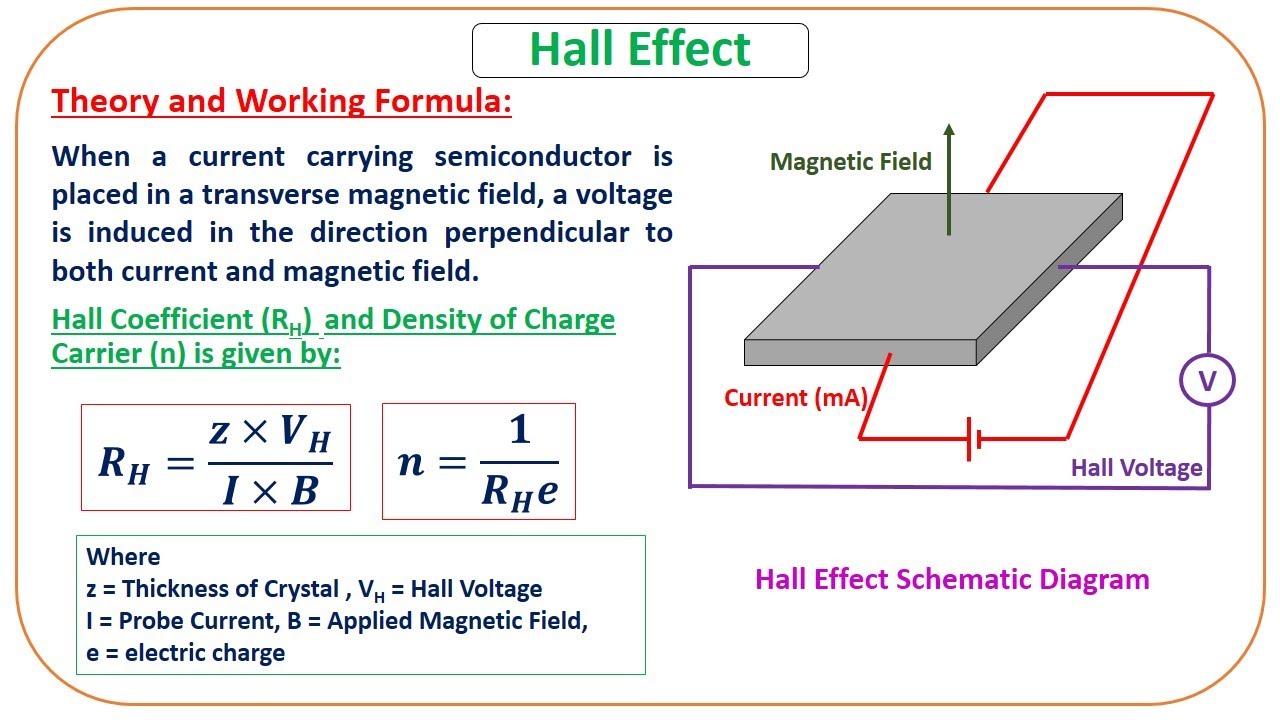
Hall Effect Experiment Youtube
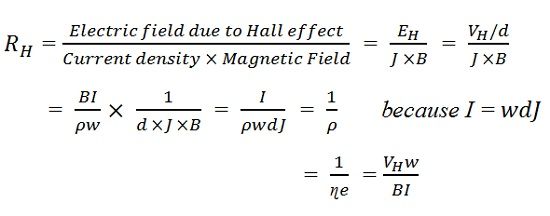
What Is Hall Effect Hall Angle Applications Of Hall Effect Electronics Coach

Hall Resistance An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
![]()
Hall Effect Hall Effect In Conductor N Type Semiconductor And P Type Semiconductor

Carrier Concentration Of Metal Using Hall Effect Experiment Youtube
![]()
Untitled

In A Hall Effect Experiment Express The Number Density Of Charge Carriers In Terms Of The Hall Effect Electric Field Magnitude E The Current Density Magnitude J And

Hall Effect Explained Electric Magnetic Field Drift Velocity Charge Density Calculations Youtube